Atomic Model
Atomic Model: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Atomic Model, Brief History of Atomic Structure Upto Bohr Model, The Thomson Model, Rutherford Experiment, Interpretation of Rutherford Experimental Results, Rutherford Model of Atom, etc.
Important Questions on Atomic Model
In Rutherford's experiment, a thin gold foil was bombarded by alpha particles. If Thomson's "Plum Pudding Model" of the atom were correct, what would have been the outcome of the experiment?
An $\alpha$ particle with energy approaches a stationary nucleus of . Assuming both of them to be point particles, the closest it will be able to come to the nucleus is
In a Davisson-Germer experiment, Helium atoms were used in place of electrons. What should be the energy of Helium so that a strong peak of scattered He appears at an angle of as was the case with electrons having an energy of (Take mass of atoms to be times the mass of electrons)
In Rutherford scattering experiment, the correct angle of scattering of α− particles for impact parameter equal to zero is
In Rutherford's experiment, the alpha particles that come closer to the nuclei are
Out of the following statements regarding Rutherford's model, which of the following is/are correct?
a. Most of the space inside an atom is empty.
b. The electrons revolve around the nucleus under the influence of coulomb force acting on them.
c. Most part of the mass of the atom and its positive charge are concentrated at its centre.
d. The stability of atom was established by the model.
Velocity of electron orbiting around nucleus of hydrogen atom is proportional to radius (r)
Radius of the smallest orbit of hydrogen atom is
The gravitational force between a -atom and another particle of mass will be given by Newton's law , where is in metre and
Geiger-Marsden experiment is related with the size of the-
A proton of mass and charge is projected from a very large distance towards an -particle with velocity Initially -particle is at rest, but it is free to move. If gravity is neglected, then the minimum separation along the straight line of their motion will be
A beam of fast moving alpha particles were directed towards a thin film of Gold. The parts and of the transmitted and reflected beams corresponding to the incident parts and of the beam are shown in the adjoing diagram. The number of alpha particles in
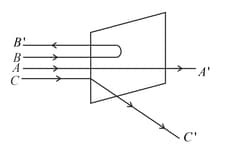
In Rutherford's experiment, an -particle of mass and charge moves at high speed , along the -axis. It is initially near , and it ends up near The gold nucleus having charge is fixed at the point . As the -particle passes the stationary nucleus, its -component of velocity does not change appreciably, but it acquires a small velocity in the -direction. The angle through which the -particle is deflected is,
On which of the following factors does the trajectory of an alpha particle depend?
The significant result deduced from the Rutherford's scattering experiment is that
What is the conclusion of Rutherford’s alpha particle scattering experiment ?
An atom is electrically neutral because there are
